1、线程的状态
线程有5种状态:初始化、可运行、运行中、阻塞、销毁。
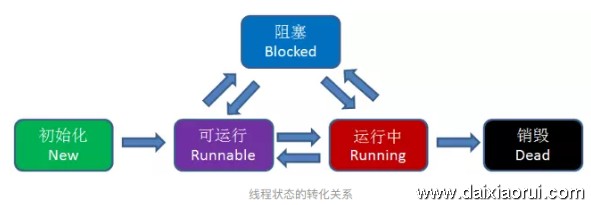
①初始化:创建一个线程。
②可运行:执行完创建工作,线程变进入“可运行”的状态,即等待CPU时间碎片(执行权)。
③运行中:得到CPU执行权后,程序变为“运行中”的状态,此时可以转变为“可运行”的状态(一个时间碎片执行完后),或者“阻塞”的状态(等待网络或者磁盘处理)。
④阻塞:当发生I/O时,就进入了“阻塞”状态。
⑤销毁:线程生命周期结束。
2、c语言pthread_create()
创建线程函数。
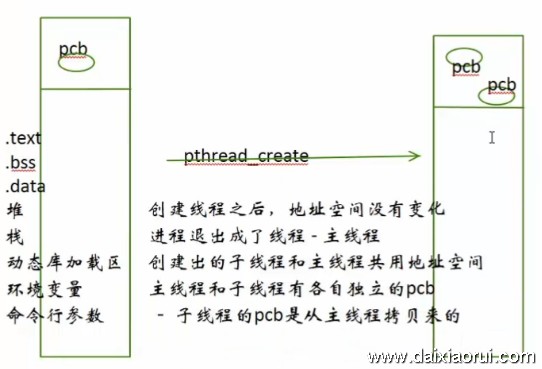
PCB:进程控制块 (Processing Control Block)
它存放着操作系统用于描述进程情况及控制进程运行所需的全部信息。
更多关于PCB的信息:https://blog.csdn.net/Duc_Duke/article/details/98482333
(深入理解计算机系统) bss段,data段、text段、堆(heap)和栈(stack): https://www.cnblogs.com/yanghong-hnu/p/4705755.html
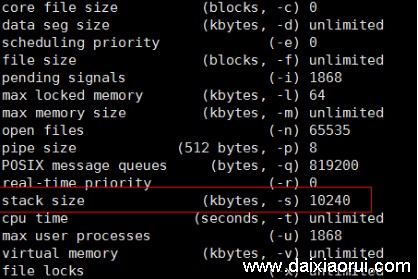
ulimit -a查看栈区大小。
linux和windows下的线程原理是不一样的,linux下的线程就是轻量级的进程,对于内核来说,线程就是进程。
线程相关函数:
(1)创建线程:pthread_create()
(2)退出线程:pthread_exit();
3、线程demo
注意,用gcc命令编译的时候需要带上-lpthread参数。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <pthread.h>
void* myfunc(void* arg)
{
printf("child thread id: %lu\n", pthread_self());
return NULL;
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
//创建一个子线程
pthread_t thread_id;
int res = pthread_create(&thread_id, NULL, myfunc, NULL);
if (res != 0) {
printf("error code: %d\n", res);
printf("error info: %s\n", strerror(res));
return 0;
}
printf("parent thread id: %lu\n", pthread_self());
//回收线程
pthread_join(thread_id, NULL);
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}查看线程信息:
Linux/Unix和Windows中多线程的区别:https://blog.csdn.net/QuitePig/article/details/8022875
4、查看线程
(1) windows下

(2) linux下
ps -Lf 进程号